Player Movement Functions
Player movement in this game is complicated. The usual two-dimensional side-scrolling controls are present – walk left/right, jump, fall, and the player can usually look up and down to scroll the screen some distance. Some map tiles permit passage if they are jumped through, but prevent movement if something falls onto them. Some surfaces are sloped at a 45° angle, and other surfaces can move and carry the player along with them. The player may find a Scooter that allows them to fly freely to any area of the map.
On top of all that, the player has an unusual movement ability in that they can cling to certain vertical walls by pushing into them while jumping or falling, then repeatedly jump and re-cling to climb great distances. Various surfaces in the game are slippery and work against efforts to cling or walk uphill.
The player’s primary defense mechanism is movement-based, and involves falling onto the top of an enemy actor (an action called pouncing). Actors that have been pounced cause the player to recoil some distance back up into the air. Other actors may push the player around the map with a force that cannot be counteracted by user input.
Ground Rules
The regular walk speed of the player is one tile per game tick. The rise and fall speeds may be either one or two tiles per game tick, depending on how much “momentum” the move has. The player moves one tile in both horizontal and vertical directions while walking over sloped tiles, making the effective speed over those areas √2 tiles per game tick. Look up/down moves one tile per game tick, while view centering typically moves at a speed that matches what the player is doing.
The player may enter any empty space of the map provided the leading edges of all the player sprite tiles move into clear space. The player may also move into areas occupied by map tiles provided the tile attributes specify that all the involved tiles are passable in that direction.
Begging Permission and Asking Forgiveness
There are two movement paradigms that can be used to determine if a proposed player move is legal. Code can ask for permission (or look before leaping):
/* Check if the player can move one tile right, and if so, move there. */
if (TestPlayerMove(DIR4_EAST, playerX + 1, playerY) == MOVE_FREE) {
playerX++;
}
Or it can beg forgiveness:
/* Move the player right. If they moved into a bad spot, revert the move. */
playerX++;
if (TestPlayerMove(DIR4_EAST, playerX, playerY) != MOVE_FREE) {
playerX--;
}
Both are acceptable forms that produce the correct answer. One’s a little less dense, one’s a little more mild-mannered in terms of keeping the global state undisturbed. This game uses both approaches interchangeably, and it’s important to recognize both patterns and understand what the code is trying to do: The player is at some X position, they want to move one tile toward DIR4_EAST to X + 1, and the legality of this move must be decided before the move is realized.
TestPlayerMove()
The TestPlayerMove() function tests if the player sprite is permitted to move in the direction specified by dir and enter the map tiles around x_origin and y_origin. Depending on the result of the test, one of the MOVE_* constants is returned according to the following table:
| Return Value | Description |
|---|---|
MOVE_FREE | The move is permitted; none of the map tiles the player touches in the new location interfere with movement in the specified direction. |
MOVE_BLOCKED | The move is forbidden; at least one of the map tiles the player touches in the new location forbids movement in the specified direction. |
MOVE_SLOPED | The move is permitted as with MOVE_FREE, however at least one tile at the player’s feet is sloped and a subsequent vertical adjustment will be required to keep the player at the correct height. |
This function always clears the global isPlayerSlidingEast and isPlayerSlidingWest flags, and the only time they could be re-enabled is when a dir of DIR4_SOUTH is passed. pounceStreak may also be zeroed in this direction.
canPlayerCling is always recalculated whenever dir is DIR4_WEST or DIR4_EAST.
word TestPlayerMove(word dir, word x_origin, word y_origin)
{
word *mapcell;
word i;
isPlayerSlidingEast = false;
isPlayerSlidingWest = false;
Every call to this function clears both the isPlayerSlidingEast and isPlayerSlidingWest flags (although not every path through the function is capable of re-enabling either of them).
switch (dir) {
The entirety of this function is arranged as a switch statement, with each case label handling one of the four possible DIR4_* values.
case DIR4_NORTH:
if (playerY - 3 == 0 || playerY - 2 == 0) return MOVE_BLOCKED;
This case handles moves in the DIR4_NORTH direction, for situations where the player sprite is rising vertically on the screen.
playerY represents the vertical position of the bottom row of player sprite tiles, or colloquially, the player’s feet. The player sprite is always five tiles tall no matter which sprite frame is being shown. playerY - 3 is the second row of tiles from the top, while playerY - 3 is the row of tiles at the center of the sprite. If either of these expressions evaluates to zero, the player is partially off the top edge of the map already and there is absolutely no reason that they should be permitted to move any higher. MOVE_BLOCKED is returned in this case.
Note:
The offsets chosen here will allow the topmost row of player sprite tiles to leave the map. This allows their hair (but not the face) to leave view.
The bottom two rows are not tested here, due to the assumption that the player never moves vertically more than two tiles per game tick. Assuming everything is working properly, the upper half of the sprite will get caught before the bottom rows ever need to be considered.
mapcell = MAP_CELL_ADDR(x_origin, y_origin - 4);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (TILE_BLOCK_NORTH(*(mapcell + i))) return MOVE_BLOCKED;
}
break;
The MAP_CELL_ADDR() returns a pointer to the word of mapData that represents the horizontal position in x_origin and the vertical in y_origin minus four. Since y_origin represents the tile containing the player’s feet, we need to move up four rows to locate the tile containing the top of their head. The mapcell pointer gets the address of the map tile containing the top-left tile of the player’s sprite.
The for loop iterates i from zero to two, each iteration representing an increasing horizontal position across the top of the sprite. mapcell + i is the address of that tile, and the dereferenced value is passed through TILE_BLOCK_NORTH() to determine if the tile in this location blocks northward movement. If any tile does, MOVE_BLOCKED is immediately returned without considering any additional tile positions.
If all three tiles at the top of the player’s sprite permitted the move, break jumps to the end of the function, where MOVE_FREE is ultimately returned.
case DIR4_SOUTH:
if (maxScrollY + SCROLLH == playerY) return MOVE_FREE;
mapcell = MAP_CELL_ADDR(x_origin, y_origin);
This is the case for the DIR4_SOUTH direction.
The sum of maxScrollY plus SCROLLH represents the first tile past the bottom of the visible map. There is actually a hidden row of map tiles at this elevation, but it is garbage and shouldn’t be considered as something that could interact with the player. (See the map format page for details.) In the case where the playerY is passing through this garbage row, MOVE_FREE is unconditionally returned to prevent anything from interfering randomly.
The mapcell pointer is set up as in the DIR4_NORTH case, except here there are no corrections done to y_origin since we actually want to look at the tiles by the player’s feet here.
if (
!TILE_BLOCK_SOUTH(*mapcell) &&
TILE_SLOPED(*mapcell) &&
TILE_SLIPPERY(*mapcell)
) isPlayerSlidingEast = true;
if (
!TILE_BLOCK_SOUTH(*(mapcell + 2)) &&
TILE_SLOPED(*(mapcell + 2)) &&
TILE_SLIPPERY(*(mapcell + 2))
) isPlayerSlidingWest = true;
Here we are testing for tiles that are both sloped and slippery. The game needs to know about this condition to force-slide the player down the icy hills.
In order for the player to slide east, the tile value at the player sprite’s bottom left corner (*mapcell) needs to not block southward movement (!TILE_BLOCK_SOUTH()), it must be sloped (TILE_SLOPED()) and it must be slippery (TILE_SLIPPERY()). If all three of these conditions match, isPlayerSlidingEast is set to true.
isPlayerSlidingWest is set exactly the same way, except the tile being tested is at the player sprite’s bottom right corner, *(mapcell + 2).
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (TILE_SLOPED(*(mapcell + i))) {
pounceStreak = 0;
return MOVE_SLOPED;
}
if (TILE_BLOCK_SOUTH(*(mapcell + i))) {
pounceStreak = 0;
return MOVE_BLOCKED;
}
}
break;
As with the DIR4_NORTH case, the bottom edge of the player’s sprite is tested against each map tile in a three-iteration loop. The tests start at the player’s bottom left tile (mapcell) and move right as i increases.
If any of the tiles the player is entering are sloped (TILE_SLOPED()) the player is considered to be standing on solid ground, which clears the running pounceStreak counter. MOVE_SLOPED is returned in this instance.
Otherwise if the tile was not sloped, but was solid in this direction (TILE_BLOCK_SOUTH()), the player is also considered to be on solid ground and pounceStreak is cleared. MOVE_BLOCKED is returned to indicate the prohibited move.
If all three tiles at the bottom of the player’s sprite permitted the move, break jumps to the end of the function, where MOVE_FREE is ultimately returned.
case DIR4_WEST:
mapcell = MAP_CELL_ADDR(x_origin, y_origin);
canPlayerCling = TILE_CAN_CLING(*(mapcell - (mapWidth * 2)));
This is the case for the DIR4_WEST direction.
The mapcell pointer is set up just like it was in the DIR4_SOUTH case, referring to the tile at the bottom left of the player’s sprite position.
mapcell - (mapWidth * 2) is a bit of linear addressing. The map is conceptually a two-dimensional array with a horizontal size of mapWidth and a not-relevant-right-now height. In actuality it’s a one-dimensional array of tile elements in row-major order. Each single-element step represents a move in the horizontal direction, while a step of mapWidth represents a vertical move to the same column in an adjacent row. Subtracting mapWidth * 2 from any tile position selects the location two tiles above. The value being dereferenced here is the map tile that is two rows above mapcell, which is the left tile in the middle row of the player’s sprite, approximately where the suction cup hands are depicted on a west-facing player sprite.
TILE_CAN_CLING() determines if the tile at the player sprite’s hand is clingable, and the result is stored in canPlayerCling.
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (TILE_BLOCK_WEST(*mapcell)) return MOVE_BLOCKED;
if (
i == 0 &&
TILE_SLOPED(*mapcell) &&
!TILE_BLOCK_WEST(*(mapcell - mapWidth))
) return MOVE_SLOPED;
mapcell -= mapWidth;
}
break;
The main test is structured as a five-iteration for loop, each iteration testing the next higher tile at the left edge of the player’s sprite. If any tile blocks the move (TILE_BLOCK_WEST()), MOVE_BLOCKED is returned.
On the first iteration (only), if the examined tile is sloped (TILE_SLOPED()) and the tile directly above it permits movement in our current direction (!TILE_BLOCK_WEST()) the MOVE_SLOPED value is returned and testing stops. This condition means that the player is walking up a hill and the eventual increase in elevation will not cause them to enter a tile that would refuse the move.
Otherwise mapcell is reduced by mapWidth, selecting the next higher tile, and the loop keeps going. If the loop runs to completion without finding any blocking tiles, break jumps to the end of the function, where MOVE_FREE is ultimately returned.
case DIR4_EAST:
mapcell = MAP_CELL_ADDR(x_origin + 2, y_origin);
canPlayerCling = TILE_CAN_CLING(*(mapcell - (mapWidth * 2)));
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (TILE_BLOCK_EAST(*mapcell)) return MOVE_BLOCKED;
if (
i == 0 &&
TILE_SLOPED(*mapcell) &&
!TILE_BLOCK_EAST(*(mapcell - mapWidth))
) return MOVE_SLOPED;
mapcell -= mapWidth;
}
break;
This is the case for the DIR4_EAST direction. It’s identical to the DIR4_WEST case, except the initial mapcell position is targeting the bottom right tile of the player’s sprite at x_origin + 2. (The inner tests use TILE_BLOCK_EAST() as well.)
}
return MOVE_FREE;
}
In the fallback case, if nothing inside any of the earlier branches returned anything, MOVE_FREE is the return value.
Dancing on the Ceiling
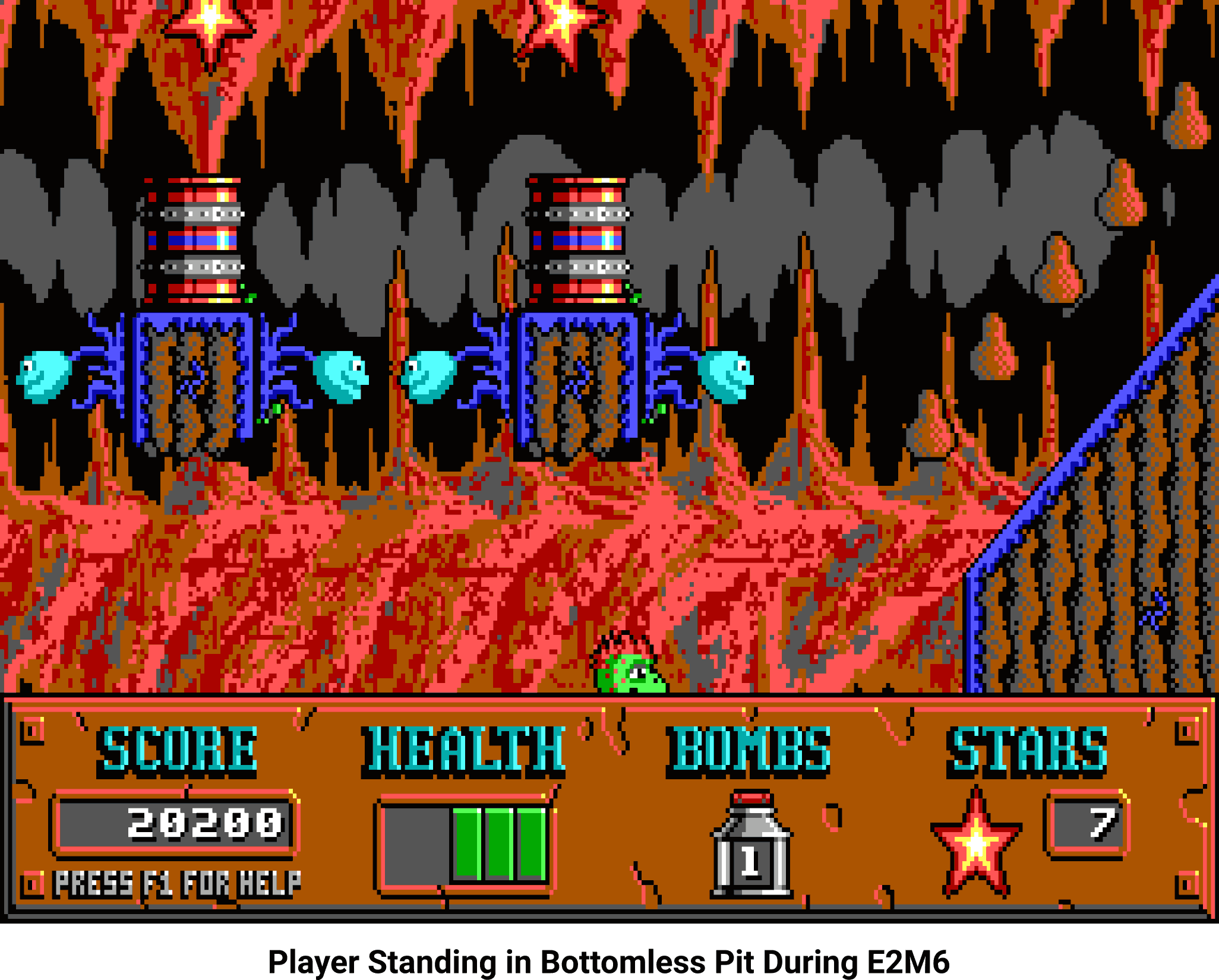
This shouldn’t happen:
When playing E2M6, it does. This map exhibits a bug where the player can’t die in any of the bottomless pits, and is able to walk and jump in those areas as if they were solid ground. To get to the bottom of this behavior it’s necessary to understand exactly what happens when TestPlayerMove() makes its decisions. When called with DIR4_SOUTH as its first argument, this is approximately the C code that runs:
if (maxScrollY + SCROLLH == playerY) return MOVE_FREE;
mapcell = MAP_CELL_ADDR(x_origin, y_origin);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (TILE_BLOCK_SOUTH(*(mapcell + i))) {
pounceStreak = 0;
return MOVE_BLOCKED;
}
}
return MOVE_FREE;
First a check is made to see if the player’s feet entered into the row of garbage tiles that always occupy the bottom row of each map. The map format page has more information, but the long and short is that the bottom row of tiles (stored at the end of the map data) is incomplete at the right side and on most maps the whole row contains incomplete or nonsensical tile data. The game never allows this row to be scrolled into view, and if the player’s position is already inside this row (maxScrollY + SCROLLH) the move is unconditionally permitted (MOVE_FREE).
At every other Y position, whether in a pit or not, mapcell points to the map tile memory address at the x_origin and y_origin positions where the player wants to move. In a three-iteration for loop (one iteration per player sprite tile horizontally), each tile to the right of that original x_origin position gets tested, and if any tile blocks southward movement the MOVE_BLOCKED value is returned. If nothing blocks, MOVE_FREE is returned. This tests every map tile that the bottom of the player’s sprite could potentially touch.
Interestingly, the maxScrollY-involved check uses the current value of playerY and not the passed y_origin value that the rest of the movement calculations use. Typically TestPlayerMove() is passed a speculative location where the player wants to move, but this check uses the place where they already are. It calls into question how the player got into this row in the first place.
Over in MovePlayer the rough gist of player falling is:
if (isPlayerFalling) {
playerY++;
if (TestPlayerMove(DIR4_SOUTH, playerX, playerY) != MOVE_FREE) {
isPlayerFalling = false;
playerY--;
}
}
This is heavily simplified, but the important bit is that the player moves down first, then the position where they ended up is checked, and if that tile didn’t permit the action the move gets reverted. Once the player moves into the garbage row, TestPlayerMove() always returns MOVE_FREE and the move here is never unwound.
So that explains what happens when the player touches the edge of the map, and how they are permitted to pass through unviewable garbage data, but it doesn’t really get us any closer to understanding the bug.
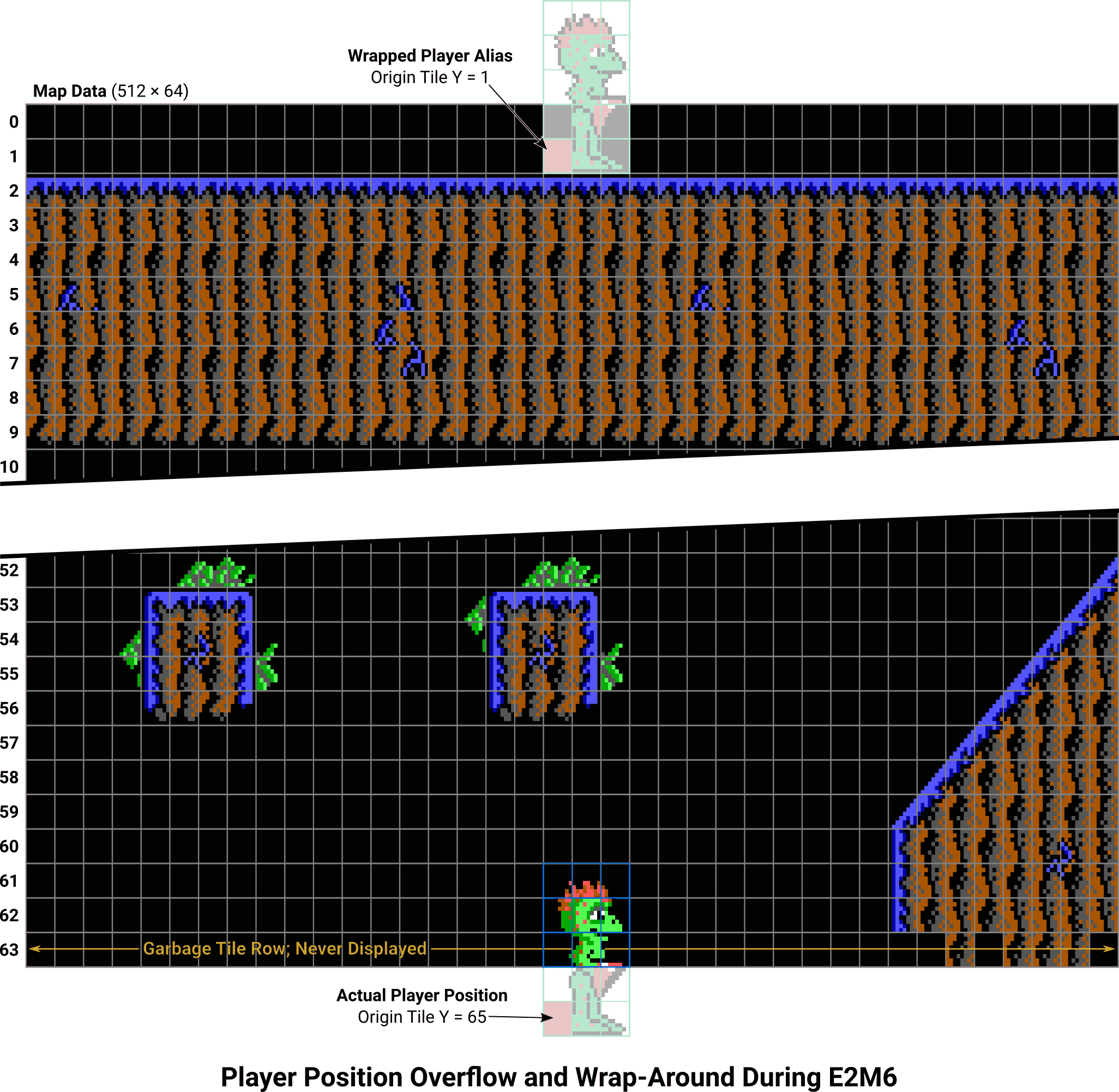
When the player falls an additional tile, things get interesting fast. The player’s Y position is now no longer in the final row of garbage tiles, it’s past it. On a map that is (e.g.) 64 tiles high, we’re now in the 65th tile row. The game doesn’t really test for this condition in the general sense, it just steamrolls ahead with the Y value, assuming it must point to some valid map data. This ultimately reads past the end of a buffer, which is undefined behavior in C, therefore the compiler (and the program) can do any damned thing it desires.
We also need to remember the memory model of the IBM PC, and specifically the way the Intel x86 processors address memory in real mode. Being 16-bit processors, the largest value that can be handled in a register or memory operand is 16 bits wide, in the range 0–65,535. In order to unambiguously refer to more than 64 KiB of memory, addresses are split into paragraph-sized segments and single-byte offsets. The segment values cover 1,024 KiB of memory with 16-byte granularity (that’s the size of one paragraph), and individual bytes can be accessed by adding an offset to that.
Generally C pointers acquired by Borland’s malloc() will set the segment address to the first paragraph containing the data and the offset gets a value between zero and 15 to point to the first byte exactly. Any pointer math is implemented by moving the offset address away from the fixed segment address. Remember though that the offset is still an unsigned 16-bit value under the hood, and if it should overflow it goes right back to the beginning of the same segment.
So what does mapcell = MAP_CELL_ADDR(x_origin, y_origin) do with an excessive y_origin? Un-macroing that, we get:
mapcell = mapData.w + (y_origin << mapYPower) + x_origin;
After a quick trip through the compiler and then a disassembler:
mov ax,[bp+10] ; [function argument y_origin]
mov cl,[0x4b70] ; [mapYPower]
shl ax,cl
shl ax,1
les bx,[0x4b6a] ; [mapData]
add bx,ax ; ES:BX = mapData + (y_origin << mapYPower)
mov ax,di ; DI has our copy of function arg x_origin
shl ax,1
add bx,ax ; ES:BX += x_origin
mov [bp-2],es
mov [bp-4],bx ; [mapcell] = ES:BX
In our example’s 64 tile-high map, the width is 512 tiles by definition (the product must always equal 32,768). mapYPower is therefore 9. Lets say the player has continued to fall and is now interacting with tiles on (zero-indexed) row 65, way outside the legal Y range of 0–63. AX takes 65, CL is 9, and the first shl produces 33,280 in AX. What this is saying is that, to access tiles on row 65 of a map with these dimensions, we need to skip over 33,280 linear tiles of data to select that row.
Each tile is two bytes (owing to the pointer referring to a word type in the way it is used here) so we need to double 33,280 to get something we can use as a memory offset. The compiler implements that as a shl by one, which is a handy speed optimization.
That shl is where the cold realities of the processor whack us. We overflow the 16-bit register, wrap past zero, and AX becomes 1,024. We end up with the same result that we would’ve had if we had entered the function with y_origin set to 1.
les bx,... sets ES to the segment address of mapData and BX to the offset to its first byte. The result in AX, right or wrong, increases the offset in BX and then x_origin increases it further, and nothing remembers whether or not anything overflowed.
In terms of map space, it’s a reasonable behavior. If you read a piece of paper from left to right, then top to bottom, eventually you’re going to find yourself at the bottom-right corner with nowhere else to go. The only logical place to jump is back to the top-left of something. It also makes perfect sense from the standpoint of the processor, because that conceptual piece of paper is mapped onto a 64 KiB range of offset values that wraps the exact same way.
When the player falls into a bottomless pit, most of the game’s logic has no trouble with the excessive Y position, but the map intersection calculations behave as if the player wrapped around and started falling into the top of the sky in row zero. And actually, most of the time this isn’t a problem – maps with bottomless pits tend to also have vast unbounded open sky in the top few map rows. But E2M6 is different: It evokes a sort of cave vibe, complete with a line of solid ground at the top of the visible scroll area to suggest that you’re in a system of worm tunnels underground.
Pictures say more than words:
And that’s the cause: A buffer over-read wraps around harmlessly on the specific hardware the game was written for, allowing the design of an unrelated area of the map to influence whether or not the bottomless pits function as intended.
SetPlayerPush()
The SetPlayerPush() function configures the global game state to cause the player to be pushed in a direction dir at speed tiles per game tick for a total duration of max_time game ticks. During this time, the player sprite will be drawn using force_frame as the frame number. If the abortable flag is set, the player can cancel the effect of the push by jumping. If the blockable flag is set, the push will consider and stop at any solid map tiles encountered along the way. Conventional actor pushes use the blockable flag. The pipe system uses a non-blockable push to move the player around.
Nothing in the unmodified game sets the abortable flag, and all pushes use the constant speed of 2.
void SetPlayerPush(
word dir, word max_time, word speed, word force_frame, bool abortable,
bool blockable
) {
playerPushDir = dir;
playerPushMaxTime = max_time;
playerPushTime = 0;
playerPushSpeed = speed;
playerPushForceFrame = force_frame;
isPlayerPushAbortable = abortable;
isPlayerPushed = true;
scooterMounted = 0;
isPlayerPushBlockable = blockable;
isPlayerRecoiling = false;
playerRecoilLeft = 0;
ClearPlayerDizzy();
}
The push state is represented by eight global variables:
playerPushDir(set todir) records theDIR8_*direction the push moves the player in.playerPushMaxTime(set tomax_time) represents the maximum number of game ticks the push should be allowed to run before it auto-cancels.playerPushTime(initialized to zero) tracks the number of game ticks that the player has been pushed for. This value will increment from zero up to the maximum inplayerPushMaxTime.playerPushSpeed(set tospeed) records the number of tiles the player should move during each game tick.playerPushForceFrame(set toforce_frame) controls which player sprite frame is drawn during the course of the push. This is usually one of two availablePLAYER_PUSHEDframes for regular actor-involved pushes andPLAYER_HIDDENwhen inside pipes.isPlayerPushAbortable(set toabortable) tracks whether this push should be able to be canceled early by using the “jump” command.isPlayerPushed(set to true) is the main flag that enables the per-tick pushing logic.isPlayerPushBlockable(set toblockable) tracks whether this push should consider any movement-blocking walls it encounters.
Separately from the push-specific variables, this function zeroes the scooterMounted variable to knock the player off any scooter they may be riding on. isPlayerRecoiling and playerRecoilLeft are both cleared to cancel any upward jump/recoil energy the player has amassed, and ClearPlayerDizzy() removes any dizzy effects the player is dealing with.
ClearPlayerPush()
The ClearPlayerPush() function immediately cancels any push the player may be experiencing, and returns the game state back to regular player control.
void ClearPlayerPush(void)
{
isPlayerPushed = false;
playerPushDir = DIR8_NONE;
playerPushMaxTime = 0;
playerPushTime = 0;
playerPushSpeed = 0;
playerPushForceFrame = 0;
isPlayerRecoiling = false;
playerRecoilLeft = 0;
isPlayerPushAbortable = false;
isPlayerFalling = true;
playerFallTime = 0;
}
The push-specific variables isPlayerPushed, playerPushDir, playerPushMaxTime, playerPushTime, playerPushSpeed, playerPushForceFrame, and isPlayerPushAbortable are all set to zero here, erasing any evidence that a previous push may have left behind. (The isPlayerPushBlockable is left alone, which may be a small but inconsequential oversight.)
In order to return the player back to regular control, this function sets isPlayerFalling to true, which causes later movement code in MovePlayer to check if the player needs to fall any distance to contact the ground. In a typical horizontal-only push, it will be apparent that the player is already on the ground and no further adjustment will be required. Otherwise gravity will pull them down as expected.
To ensure sanity of the global state, isPlayerRecoiling, playerRecoilLeft, and playerFallTime are all cleared before returning control to the regular movement code. This is cheap insurance to make sure there are no abrupt movements due to the variables holding stale values.
MovePlayerPush()
The MovePlayerPush() function handles one game tick of player push movement. isPlayerPushed must be true for this to do anything, otherwise it behaves as a no-op.
Push configuration and the associated global state is described in SetPlayerPush(). If the configured “speed” value is greater than one, this function will move the player multiple tiles in the configured direction before returning.
void MovePlayerPush(void)
{
word i;
bool blocked = false;
if (!isPlayerPushed) return;
if (cmdJump && isPlayerPushAbortable) {
isPlayerPushed = false;
return;
}
If isPlayerPushed is false, there is not currently an active push and this function should do nothing. return early in this case.
Otherwise if cmdJump is true, the user is currently holding the jump key/button down. If isPlayerPushAbortable is also true, the active push was configured such that the player is permitted to “jump out” of an active push. In this case, isPlayerPushed is cleared to immediately cancel the push, and an early return is taken. The player regains control at this point.
Note: None of the pushes in the retail game are set up with an abortable push, so this branch is never taken. The fact that
ClearPlayerPush()is not called here suggests that maybe this was an early idea whose implementation didn’t mature with the rest of the feature.
for (i = 0; i < playerPushSpeed; i++) {
The “speed” of a push is implemented by repeating the actual movement code multiple times, one iteration per tile moved. All pushes in the retail game produce a playerPushSpeed of 2, so this for loop body always runs twice per call. (The i variable is not used for anything beyond maintaining loop state.)
if (
playerX + dir8X[playerPushDir] > 0 &&
playerX + dir8X[playerPushDir] + 2 < mapWidth
) {
playerX += dir8X[playerPushDir];
}
The playerPushDir value is one of the DIR8_* constants, which can be decomposed using the dir8X[] array into a X change in the range -1 – 1. This value is added to playerX to move the player. This is done conditionally, requiring the result to be larger than zero (so, not off the left map edge). The right edge of the player’s sprite (which is the point two tiles right of playerX) must also be smaller than mapWidth to keep the player inside the right map edge.
playerY += dir8Y[playerPushDir];
playerY is modified the same way (using dir8Y[] this time) but without the bounds-checking. Broadly, the game gets away with this because vertical pushes only occur when interacting with pipe actors that are in fixed locations placed by the map author. It’s essentially impossible for a pipe actor to knock the player off the top/bottom of the map, while it’s quite plausible that a wandering actor can follow the player to a location where a horizontal push would reach a map edge.
if (
scrollX + dir8X[playerPushDir] > 0 &&
scrollX + dir8X[playerPushDir] < mapWidth - (SCROLLW - 1)
) {
scrollX += dir8X[playerPushDir];
}
if (scrollY + dir8Y[playerPushDir] > 2) {
scrollY += dir8Y[playerPushDir];
}
Similar test-then-modify behavior is repeated for scrollX and scrollY for view centering purposes.
Vertical movement is limited here, but only at the top of the map. I suspect these conditions were added as problems were encountered, and none of the maps had any vertical-pushing actors near the bottom of the map to warrant adding a test for it.
if (isPlayerPushBlockable && (
TestPlayerMove(DIR4_WEST, playerX, playerY) != MOVE_FREE ||
TestPlayerMove(DIR4_EAST, playerX, playerY) != MOVE_FREE ||
TestPlayerMove(DIR4_NORTH, playerX, playerY) != MOVE_FREE ||
TestPlayerMove(DIR4_SOUTH, playerX, playerY) != MOVE_FREE
)) {
blocked = true;
break;
}
}
If isPlayerPushBlockable is true, the current push needs to be aware of movement-blocking tiles that the player might hit. The player has already moved for this iteration, so it’s entirely possible that they’re already inside a location where they should not be. The current playerX and playerY values are passed to four TestPlayerMove() calls, each testing for a blocking tile attribute in the player’s current spot. If any of the four calls returns something other than MOVE_FREE – disregarding whether or not the player was moving in a prohibited direction at all – the player is now inside the wall. The blocked flag is set, and the outer for loop is terminated with break. In the case where the push moves the player multiple tiles per call, this will stop the loop at the first tile encountered even if there would otherwise have been more iterations to follow. This ensures that the ejection code below never needs to undo more than one tile of movement in total.
Otherwise, the for loop keeps moving the player until the playerPushSpeed limit is reached.
if (blocked) {
playerX -= dir8X[playerPushDir];
playerY -= dir8Y[playerPushDir];
scrollX -= dir8X[playerPushDir];
scrollY -= dir8Y[playerPushDir];
ClearPlayerPush();
If the previous loop ended because a wall was hit, blocked will be true and this code executes. This simply reverses the most recent addition performed on playerX, playerY, scrollX, and scrollY. This should eject the player to their last-known good location before TestPlayerMove() found a blocking tile.
Technically there are multiple edge-case bugs in here because we’re not exactly replicating the conditions that wrapped each of the original additions. In practice this would really only be noticeable during a diagonal move where the player hit a screen edge along one axis before hitting a solid tile perpendicular to that.
After unwinding the move, there is no reason to continue trying to move in the original direction, so the push ends with a call to ClearPlayerPush().
} else {
playerPushTime++;
if (playerPushTime >= playerPushMaxTime) {
ClearPlayerPush();
}
}
}
In the more common case, the for loop ended naturally without blocked getting set. The player is moving freely and they haven’t touched anything that should affect the push.
playerPushTime increments once for this game tick (regardless of how many tiles the player actually moved). Once the playerPushMaxTime is reached, the push ends naturally with ClearPlayerPush().
TryPounce()
The TryPounce() function checks if all necessary player variables are in the correct state to perform a pounce on an enemy actor. If this state is correct, a caller-provided recoil amount is imparted to the player and true is returned.
This function does not care about the X/Y position of the player or any actor – this function is only concerned with the variables that control things like player rise and fall. The caller is responsible for testing the relative positions of the player and an actor, setting the pass-by-global isPounceReady according to that result.
bool TryPounce(int recoil)
{
static word lastrecoil;
if (playerDeadTime != 0 || playerDizzyLeft != 0) return false;
This function maintains a local copy of the last recoil successfully imparted, and stores it in lastrecoil. This is occasionally needed by subsequent code.
If the player is either dead (a nonzero playerDeadTime) or dizzy (a nonzero playerDizzyLeft), they are incapable of performing a pounce even if all the other aspects of their movement would have allowed it. An early return of false prevents this pounce from producing a recoil, and informs the caller that this pounce was unsuccessful.
if ((
!isPlayerRecoiling || (isPlayerRecoiling && playerRecoilLeft < 2)
) && (
(isPlayerFalling && playerFallTime >= 0) || playerJumpTime > 6
) && isPounceReady) {
Hoo boy.
If the player were already recoiling from a pounce, they would be incapable of pouncing another actor – therefore isPlayerRecoiling should be false for pouncing to proceed. In the opposite case (needlessly testing that isPlayerRecoiling is true when we already know it must be) a small exception is made for cases where playerRecoilLeft is less than two. The latter case covers the situation where the player has a nonzero playerRecoilLeft but is no longer rising – they are at the top of the parabola between recoiling and falling. In this case it should be permissible to pounce an actor, even though technically they are not done with the previous recoil.1
Separately, the player must either be falling (isPlayerFalling) or rising to near the maximum height they can reach by holding the jump key (playerJumpTime > 6). The test for a non-negative playerFallTime is always true and likely a holdover from an older implementation.
Finally, isPounceReady must also be true. The caller sets this based on whether the player is properly positioned above some actor.
lastrecoil = playerRecoilLeft = recoil + 1;
isPlayerRecoiling = true;
ClearPlayerDizzy();
To cause the player to recoil, all that’s necessary is to write a value to playerRecoilLeft and set the isPlayerRecoiling flag to true. Here the value is recoil + 1.
Why? Why not.
There doesn’t seem to be a systemic reason why the
recoilvalue needs to be increased by one; the game works correctly without the addition. It’s likely that somebody thought that the recoils all needed a bit more oomph, and it was easier to do that here rather than go through and adjust the arguments in all theTryPounce()calls.
The most recent value written to playerRecoilLeft is also stored in the local lastrecoil variable for possible later use. This variable is declared static and retains its value across calls.
ClearPlayerDizzy() has no immediate effect here – any active dizziness would involve a nonzero playerDizzyLeft which would prevent this if body from running in the first place. This does, however, cancel any queued dizziness that might be stored. This means that a player can fall an extreme distance that would normally incur a dizzy immobilization, but land on a pounceable actor before hitting the ground and suffer no dizziness at all.
if (recoil > 18) {
isPlayerLongJumping = true;
} else {
isPlayerLongJumping = false;
}
pounceHintState = POUNCE_HINT_SEEN;
If the player is recoiling a long distance (here where recoil is greater than 18, but this is not always consistent in other parts of the code) the isPlayerLongJumping flag is set to select an alternate player recoil sprite. This variable has no other effect on gameplay.
The player has clearly demonstrated their knowledge of the pouncing mechanic, so there is no reason to show them the pounce hint dialog anymore. Setting pounceHintState to POUNCE_HINT_SEEN has the same effect as the player having seen and dismissed the dialog.
if (recoil == 7) {
pounceStreak++;
if (pounceStreak == 10) {
pounceStreak = 0;
NewActor(ACT_SPEECH_WOW_50K, playerX - 1, playerY - 5);
}
} else {
pounceStreak = 0;
}
return true;
If the passed recoil is exactly seven, the pounced actor contributes to the “pounce streak” bonus. This is a 50,000 point award that is bestowed anytime the player pounces ten times without touching the ground. Only a handful of actors are set up to impart a recoil equal to seven:
- Hopping Cabbage Creature (takes one pounce)
- Ghost
- Floating Moon
- Jumping Baby Ghost
- Flying Roamer Slug
- Baby Ghost Egg (cracks when pounced or player is near)
- Baby Ghost Egg (cracks when pounced)
- Blue Ball/Parachute Creature
- Boss
- Suction Feet Creature
- Spitting Turret Creature
- Red Chomper Creature
- Pink Worm
- Translucent Pusher Robot
- Blue Bird
- Hopping Cabbage Creature (takes two pounces)
If an actor with an appropriate recoil value is being pounced, pounceStreak is incremented and, upon reaching ten, the bonus is given. NewActor() is called to insert a “Speech Bubble: Wow! 50,000 points!” (ACT_SPEECH_WOW_50K) directly above the current playerX/playerY position, and this new actor gives the bonus indirectly. pounceStreak is reset to zero as this happens, and the bonus is ready to be earned again if the map’s actors permit.
In the else case, the non-matching recoil spoils the streak and resets the pounceStreak to zero.
Since the player has successfully entered a pounce and the recoil has been imparted, a return value of true is provided to the caller.
} else if (
lastrecoil - 2 < playerRecoilLeft &&
isPounceReady && isPlayerRecoiling
) {
For this else if to be evaluated, something in the previous if’s tests must’ve failed. This can happen for a variety of reasons, but there is one specific case that this catches: When the player pounces on two similar-height actors at the same time, the first actor that gets processed will be pounced successfully and impart a recoil. By the time the other actor is processed, the player state reflects a pounce already in progress – there is no reason to start another one.
This else if catches that case – isPlayerRecoiling is true because some other actor was already pounced during this tick, isPounceReady is true because the player is lined up to pounce on this other actor as well, and playerRecoilLeft is very close to the last value that was stashed in lastrecoil. (Actually they should be identical, but this adds a bit of a fudge factor.)
ClearPlayerDizzy();
if (playerRecoilLeft > 18) {
isPlayerLongJumping = true;
} else {
isPlayerLongJumping = false;
}
pounceHintState = POUNCE_HINT_SEEN;
return true;
}
This is essentially a duplicate of the previous if body with the exception of the pounce streak bonus handling. In fact, everything that is done in here is gratuitous – the first actor already handled everything. Only the return true is significant.
return false;
}
If neither of the above branches were taken, the pounce attempt failed. The return value of false informs the caller that no recoil was imparted, and none of the pounce effects should occur.
This case is rare, but it was captured in one of the stock demo files. In episode one, when the demo reaches map four, there is a sequence of pounces at the start of the level: The player destroys five Baskets in four pounces, then continues on to pounce two Red Chomper Creatures without touching the ground. The first Red Chomper Creature is pounced while the player is still recoiling from the last Basket, even though they were no longer rising at that moment. ↩︎